Let us find out how to properly Install and Uninstall Linux Ubuntu Nvidia Drivers Fast using the Command line and also using UX/UI.
We shall learn how to install the Linux Ubuntu NVIDIA drivers from the command line, using either the
ubuntu-drivers
tool (recommended), or APT.
Device drivers literally drive everything you’re interested in–disks, monitors, keyboards, modems–everything outside the computer chip and memory. With the ubuntu-drivers command, you can install the recommended driver for the device. Installing Linux Ubuntu Nvidia Drivers is very easy on both command lines and UI. AOT is Ubuntu recommended way to install Linux Ubuntu Nvidia Drivers.
First, detect the model of your device and the recommended driver. To do so execute the following command. Please note that your output and recommended driver will most likely be different:
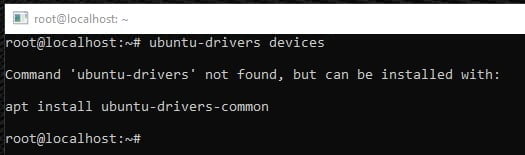
$ ubuntu-drivers devices == /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:01.0/0000:01:00.0 == modalias : pci:v000010DEd00001C03sv00001043sd000085ABbc03sc00i00 vendor : NVIDIA Corporation model : GP106 [GeForce GTX 1060 6GB] driver : nvidia-driver-390 - distro non-free driver : nvidia-driver-435 - distro non-free driver : nvidia-driver-440 - distro non-free recommended driver : xserver-xorg-video-nouveau - distro free builtin
But if you have no drivers or you have ubuntu-drivers command not working as seen below, please follow the below commands to make ubuntu-drivers work on Ubuntu Linux.
So run
$ apt ubuntu-drivers-common
You can also tun
$ sudo ubuntu-drivers autoinstall
The recommended way (ubuntu-drivers tool) to install Linux Ubuntu Nvidia Drivers
The
ubuntu-drivers
tool relies on the same logic as the “Additional Drivers” graphical tool, and allows more flexibility on desktops and on servers. So let’s continue to read about How To Correctly Install Linux Ubuntu Nvidia Drivers Fast.
The
ubuntu-drivers
tool is recommended if your computer uses Secure Boot since it always tries to install signed drivers which are known to work with Secure Boot.
Check the available drivers for your hardware
For desktop:
sudo ubuntu-drivers list
or, for servers:
sudo ubuntu-drivers list --gpgpu
You should see a list such as the following:
nvidia-driver-418-server nvidia-driver-515-server nvidia-driver-525-server nvidia-driver-450-server nvidia-driver-515 nvidia-driver-525
Installing the drivers for generic use (e.g. desktop and gaming)
You can either rely on automatic detection, which will install the driver that is considered the best match for your hardware:
sudo ubuntu-drivers install
Or you can tell the
ubuntu-drivers
tool which driver you would like installed. If this is the case, you will have to use the driver version (such as
525
) that you saw when you used the
ubuntu-drivers list
command.
Let’s assume we want to install the
525
driver:
sudo ubuntu-drivers install nvidia:525
Installing the drivers on servers and/or for computing purposes
You can either rely on automatic detection, which will install the driver that is considered the best match for your hardware:
sudo ubuntu-drivers install --gpgpu
Or you can tell the
ubuntu-drivers
tool which driver you would like installed. If this is the case, you will have to use the driver version (such as
525
) and the
-server
suffix that you saw when you used the
ubuntu-drivers list --gpgpu
command.
Let’s assume we want to install the
525-server
driver (listed as
nvidia-driver-525-server
):
sudo ubuntu-drivers install --gpgpu nvidia:525-server
You will also want to install the following additional components:
sudo apt install nvidia-utils-525-server
Optional step
If your system comes with NVswitch hardware, then you will want to install Fabric Manager and the NVSwitch Configuration and Query library. You can do so by running the following:
sudo apt install nvidia-fabricmanager-525 libnvidia-nscq-525
Manual driver installation (using APT)
Installing the NVIDIA driver manually means installing the correct kernel modules first, then installing the meta package for the driver series.
Installing the kernel modules
If your system uses Secure Boot (as most x86 modern systems do), your kernel will require the kernel modules to be signed. There are two (mutually exclusive) ways to achieve this.
Installing the pre-compiled NVIDIA modules for your kernel
Install the meta package for your kernel flavor (e.g.
generic
,
lowlatency
, etc) which is specific to the driver branch (e.g.
525
) that you want to install, and whether you want the compute vs. general display driver (e.g.
-server
or not):
sudo apt install linux-modules-nvidia-${DRIVER_BRANCH}${SERVER}-${LINUX_FLAVOUR}
(e.g.
linux-modules-nvidia-525-generic
)
Check that the modules for your specific kernel/ABI were installed by the meta package:
sudo apt-cache policy linux-modules-nvidia-${DRIVER_BRANCH}${SERVER}-$(uname -r)(e.g.
sudo apt-cache policy linux-modules-nvidia-525-$(uname -r)
)
If the modules were not installed for your current running kernel, upgrade to the latest kernel or install them by specifying the running kernel version:
sudo apt install linux-modules-nvidia-${DRIVER_BRANCH}${SERVER}-$(uname -r)
(e.g.
sudo apt install linux-modules-nvidia-525-$(uname -r)
)
Building your own kernel modules using the NVIDIA DKMS package
Install the relevant NVIDIA DKMS package and
linux-headers
to build the kernel modules, and enroll your own key to sign the modules.
Install the
linux-headers
meta package for your kernel flavor (e.g.
generic
,
lowlatency
, etc):
sudo apt install linux-headers-${LINUX_FLAVOUR}
Check that the headers for your specific kernel were installed by the meta package:
sudo apt-cache policy linux-headers-$(uname -r)
If the headers for your current running kernel were not installed, install them by specifying the running kernel version:
sudo apt install linux-headers-$(uname -r)
Finally, install the NVIDIA DKMS package for your desired driver series (this may automatically guide you through creating and enrolling a new key for Secure Boot):
sudo apt install nvidia-dkms-${DRIVER_BRANCH}${SERVER}
Installing Linux Ubuntu Nvidia Drivers in UX/UI Environment | Install Uninstall Linux Ubuntu Nvidia Drivers
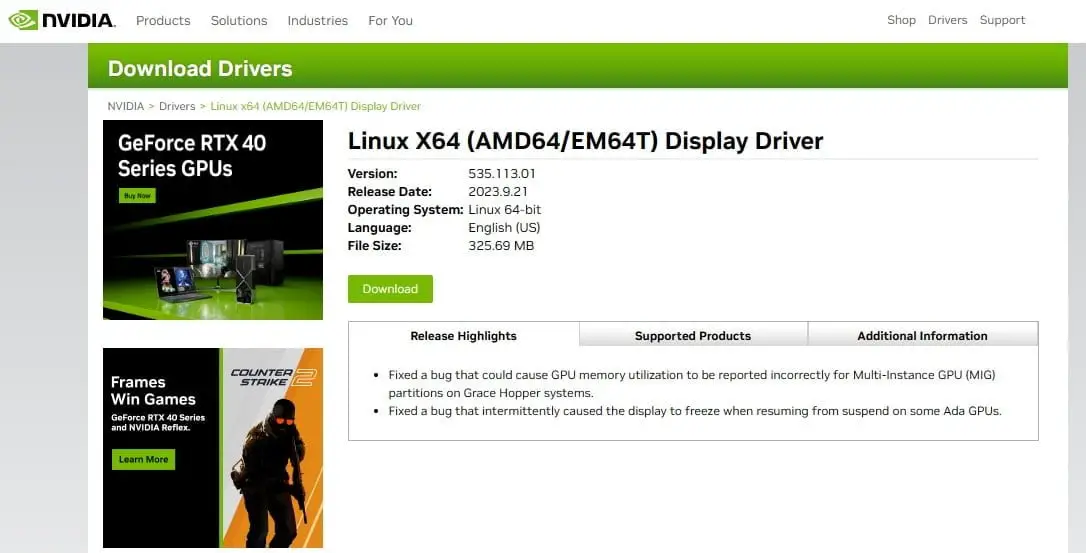
| Version: | 535.113.01 | |
| Release Date: | 2023.9.21 | |
| Operating System: | Linux 64-bit | |
| Language: | English (US) | |
| File Size: | 325.69 MB | |
Download Linux X64 (AMD64/EM64T) Display Driver
Installing the user-space drivers and the driver libraries
After installing the correct kernel modules (see the relevant section of this document), install the correct driver meta package:
sudo apt install nvidia-driver-${DRIVER_BRANCH}${SERVER}
(Optional) Installing Fabric Manager and the NSCQ library
If your system comes with NVswitch hardware, then you will want to install Fabric Manager and the NVSwitch Configuration and Query library. You can do so by running the following:
sudo apt install nvidia-fabricmanager-${DRIVER_BRANCH} libnvidia-nscq-${DRIVER_BRANCH}Uninstalling the NVIDIA drivers
Remove any NVIDIA packages from your system:
sudo apt --purge remove '*nvidia*${DRIVER_BRANCH}*'
Remove any additional packages that may have been installed as a dependency (e.g. the
i386
libraries on amd64 systems) and which were not caught by the previous command:
sudo apt autoremove


![Update the NVIDIA Drivers on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS [How To]](https://itsubuntu.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/Update-the-NVIDIA-Drivers-on-Ubuntu-22.04-LTS-How-To.jpg)

![How To Install Git On Ubuntu 22.04 LTS [2023]](https://itsubuntu.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/How-To-Install-Git-On-Ubuntu-22.04-LTS.jpg)